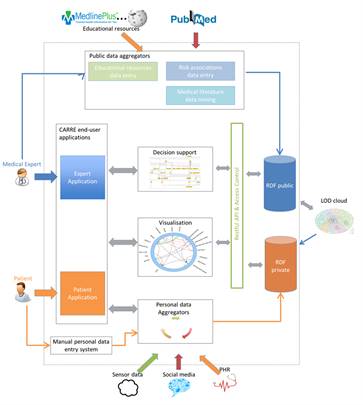
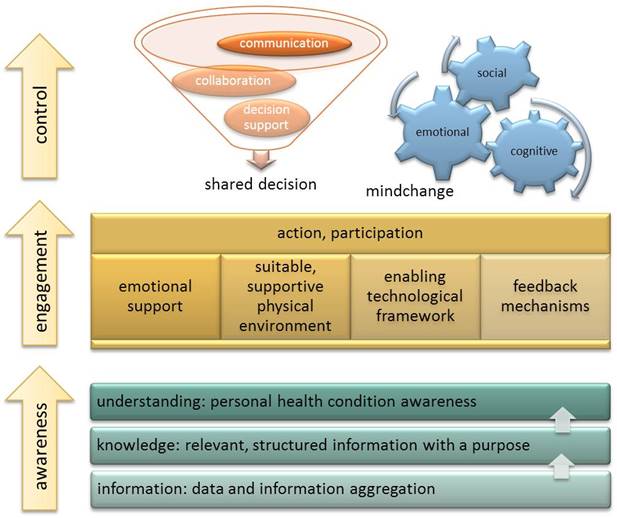
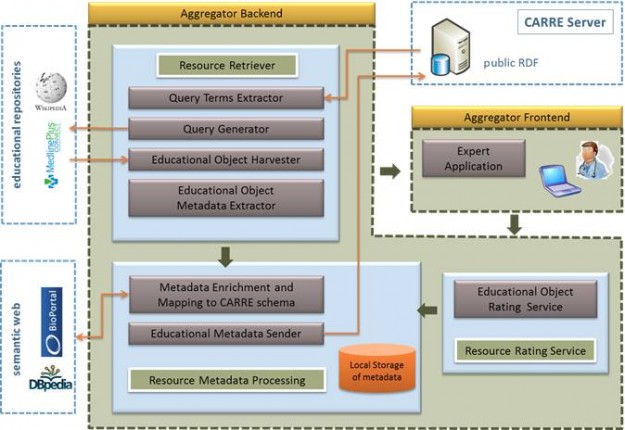
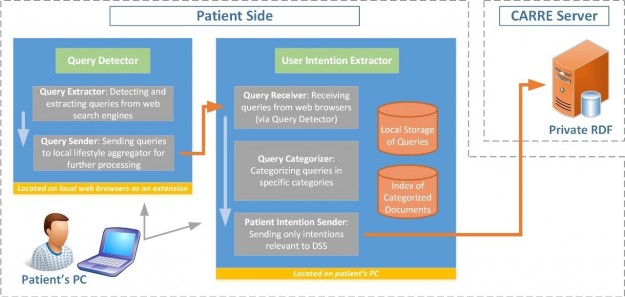
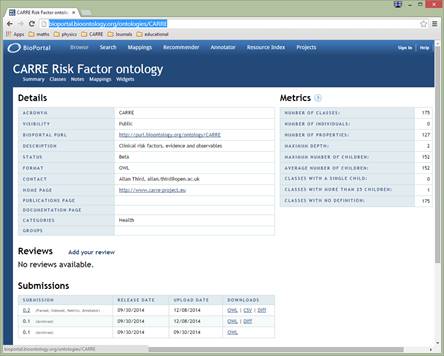
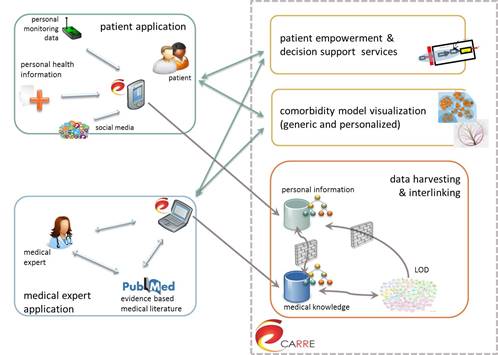
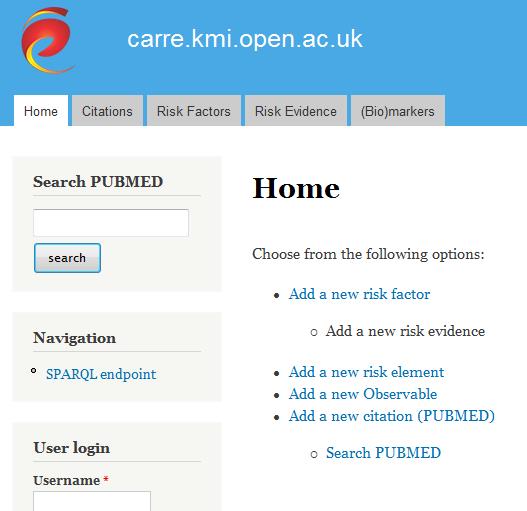
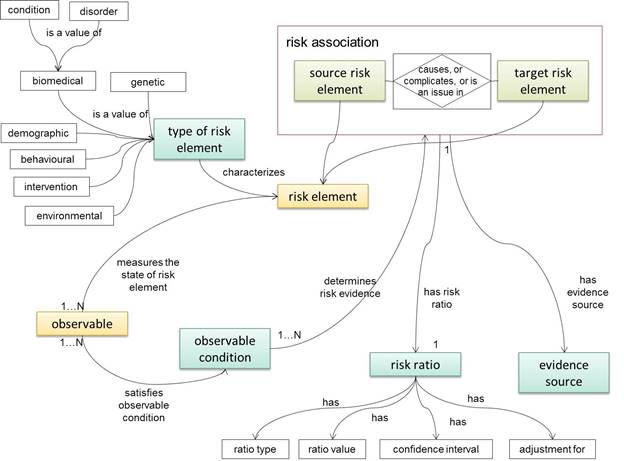
CARRE Architecture
The CARRE system architecture was developed following a component based approach. Initially, we identified (a) public and private data aggregated, used and produced by the system; and (b) major system services. Major architectural components were then designed and described. Finally, the end user perspective was captured via a number of indicative sequence diagrams to illustrate…